Polymer Congress 2018
Important Dates
Abstract Submission Opens: Dec 31, 2017
Online Registration Opens: Dec 31, 2017
Second Early bird registration: April 30, 2018
Highlights & Benefits:
Keynote Sessions on Polymer Science
Oral presentations on Polymer Science
Young Researcher Forums
Poster Presentations on Polymer Science
Video Presentations on Polymer Science
E-poster Presentations on Polymer Science
Honorable Guests Presentations
Exhibitions on Polymer Science
Free Abstract Publication & DOI
Free Lunch and Networking
Questionnaires on Polymer Science
About Conference
Euroscicon Ltd invites all the participants from all over the world to attend ‘International conference on Polymer Science and Technology 2018 ' during Jun 4-5, 2018 in London, UK, which includes prompt keynote presentations, Oral Talks, Poster Presentations and Exhibitions.
On this great gathering, Organizing Committee invites participants from all over the globe to take part in this annual conference with the theme.“Polymer Congress 2018 aims at sharing new ideas and new technologies amongst the professionals, industrialists and students from research areas of Polymer Science, Nanotechnology, Chemistry and Physics to share their recent innovations and applications in various fields and indulge in interactive discussions and technical sessions at the event. The Conference will also have a space for companies and/or institutions to present their services, products, innovations and research results.
Polymer Congress 2018 involves the tracks like Polymer Science-The Next Generation, Polymers And The Future Of Industries, Polymer Material Science And Engineering, Polymer Nanotechnology, Polymer Chemistry, Composite Polymeric Material , Advanced polymer Structures, Role of Polymers in biology and biological systems, Polymer Physics, Applications of Polymer materials.
Importance and Scope:
Polymer materials plays a vital role in our lives because of its uniqueness in properties and extended application in industries, packaging, sports, medicine, perfumes and preservatives, plastics, fuels, toys etc. Plastics are also used in the manufacture of Prosthetic devices and surgical equipment. The diversity of use is growing day by day. The history of Biopolymer is not a long one. They are beginning to emerge as a result of needing to be more responsible in taking care of the world we live in. Various reasons are associated with the research and development of polymers. The use of biopolymers and composite polymers could markedly increase as more durable versions are developed, and the cost to manufacture these bio-plastics and composites continues to go fall. Bio-plastics can replace conventional plastics in the field of their applications also and can be used in different sectors such as food packaging, plastic plates, cups, cutlery, plastic storage bags, storage containers or other plastic or composite material items you are buying and therefore can help in making environment sustainable.
Polymers have wide application in industries like aerospace, automobile etc. It also finds application in specific products like fishing rods, bicycle, sports equipment’s etc. Polymer engineering consists of many aspects of petrochemical industry and polymerization. Polymer engineering covers many aspects related to chemical engineering. Plastics are also used in the manufacture of Prosthetic devices and surgical equipment’s. The diversity of use is growing day by day. Many Polymer processing societies has been developed in recent years. The aim of these societies is to foster scientific understanding and technical innovation in polymer processing by providing a platform forum for the worldwide community of engineers and scientists in the field.
Why to attend???
International conference on Polymer Science and Technology which is going to be the biggest conference dedicated to polymer science professionals providing a premier technical forum for reporting and learning about the latest new generation technologies developed during the course of time along with discussing their applications. Events include hot topics presentations from all over the world and professional networking with industries, leading working groups and panels.
Meet Your Objective Business sector With individuals from and around the globe concentrated on finding out about Polymer science and Engineering, this is the best chance to achieve the biggest collection of members from everywhere throughout the World. Conduct shows, disperse data, meet with current, make a sprinkle with another product offering, and get name acknowledgment at this occasion. Widely acclaimed speakers, the latest methods, strategies, and the most up to date overhauls in Polymer science and Engineering are signs of this meeting.
Sessions & Tracks
Polymer Science - The Next Generation
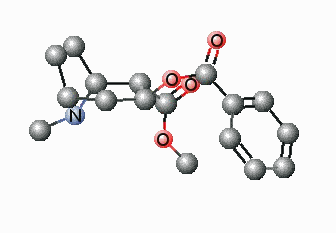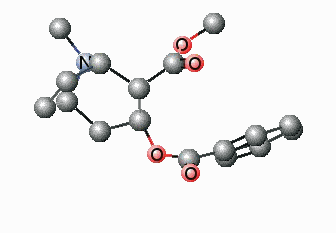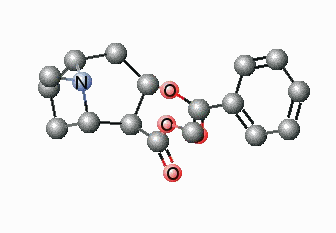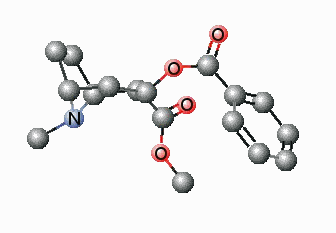
The foremost challenges in the upcoming decades will be the increase in population, the concentration of people in expansive urban centers, and globalization, and the expected change of climate. Hence, the main concerns for humans in the future will be energy & resources, food, health, mobility & infrastructure and communication. There is no doubt that polymers will play a key role in finding successful ways in handling these challenges. Polymers will be the material of the new millennium and the production of polymeric parts i.e. green, sustainable, energy-efficient, high quality, low-priced, etc. will assure the accessibility of the finest solutions round the globe. Synthetic polymers have since a long time played a relatively important role in present-day medicinal practice. Many devices in medicine and even some artificial organs are constructed with success from synthetic polymers. It is possible that synthetic polymers may play an important role in future pharmacy, too. Polymer science can be applied to save energy and improve renewable energy technologies.
·Polymers in Implants and Medical Devices
· Dental composites
·Polymers in diagnostics
·Implanted polymers for drug delivery
·Polymer dielectrics for electronics
·Polymers in compact disk technology
·Polymers for electrophotography
·Polymeric solar cells
Polymers and the future of Industries

Since the plastics industry has witnessed a spectacular growth over the last six decades, the acceleration in consumption rates of plastics has taken place in several phases since World War II. In areas of applications of plastics materials, a well-known long-standing example is electrical industries where the excellent combination of properties such as insulation characteristics, toughness, durability, flame retardation capacity has led to increasing acceptance of plastics for plugs, sockets, wire and cable insulations and for housing electrical and electronic equipment. The major polymer targeting industries of the present-day life includes building industry, packaging industries, in retorting method used for food processing industries, wood-plastic composites, polymers in corrosion prevention and control, piping systems, in automotive industries, in aerospace industries and in electrical and electronic industries.
·Thermoplastic carbonates in medical devices
·Thermoset resins for automotive, electronic, adhesives and constructions industries
·Silicone elastomers in cosmetics
·Polyesters in clothing and food packaging industries
·Polyacrylates in paints and varnishes
·Polyurethanes in cushioning, shoe sole and electrical equipment’s
·Polymer quenchants for Industrial Heat treatment
Polymer Material Science and Engineering
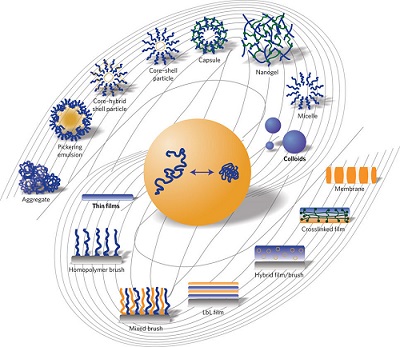
Beside metals and ceramics, the study of polymers has currently become a cornerstone of material sciences and engineering. Polymers have the capacity to solve most of the world's complex problems like Water purification, energy management, oil extraction and recovery, advanced coatings, myriad biomedical applications, building materials, and electrical applications virtually no field of modern life would be possible without polymeric materials. A Polymer Material Sciences and Engineering will provide you with a strong basis in the wide range of issues around structural and functional polymers. This multidisciplinary course is proposed in conjunction with the School of Chemistry allowing you to gain a rich understanding of both traditional commodity plastics and specialty polymers with increasing in the bio medical application and pharmaceutical industry, and in electronics and nanotechnology.
·Structure and mechanical properties of polymers
·Control and design of polymerizations
·Polymer characterization
·Polymer Processing
·Supramolecular polymers
·Conjugated polymers
Polymer Nanotechnology
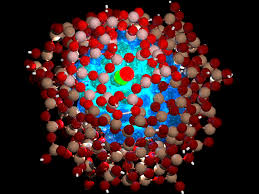
The field of Nanotechnology is one of the most popular areas for current research and development in basically all technical disciplines. This obviously includes polymer Nanotechnology which include microelectronics. Other areas include polymer-based biomaterials, Nano medicine, Nano emulsion particles; fuel cell electrode polymer bound catalysts, layer-by-layer self-assembled polymer films, electro spun nanofabrication, imprint lithography, polymer blends and Nano composites. Even in the field of nanocomposites, many diverse topics exist including composite reinforcement, barrier properties, flame resistance, electro-optical properties, cosmetic applications, bactericidal properties. Nanotechnology is not new to polymer science as prior studies before the ages of nanotechnology involved Nano scale dimensions but were not specifically referred to as nanotechnology until recently. Phase separated polymer blends often achieve Nano scale phase dimensions; block copolymer domain morphology is usually at the Nano scale level; asymmetric membranes often have Nano scale void structure, mini emulsion particles in the large field of nanotechnology, polymer matrix based Nano composites have become a prominent area of current research and development.
·Tissue engineering
·Polymer nanocomposites matrices
·Polycondensation polymerization
·Nano electronics & photonics
·Polymer films
·Bio-hybrid polymer nanofiber
·Block copolymer nanocomposites
Polymer Chemistry

Polymer chemistry is combining several specialized fields of expertise. It deals not only with the chemical synthesis, Polymer Structures and chemical properties of polymers which were esteemed by Hermann Staudinger as macromolecules but also covers other aspects of Novel synthetic and polymerization methods, Reactions and chemistry of polymers, properties and characterization of polymers, Synthesis and application of polymer bio conjugation and also Polymer Nano composites and architectures. According to IUPAC recommendations, macromolecules are considered relevant to the individual molecular chains and are the domain of chemistry. Industrial polymer chemistry has particular attention on the end-use application of products, with a smaller emphasis on applied research and preparation.
·Reactions and chemistry of polymers
·Synthesis and application of novel polymers for bio-/nanomedicine
·Supramolecular polymers
·Higher-order polymer structures
·Hydrogen bonding and the phase behavior of polymer blends and solutions
·Novel synthetic and polymerization methods
·Polymerization mechanisms and kinetics
Composite Polymeric Materials
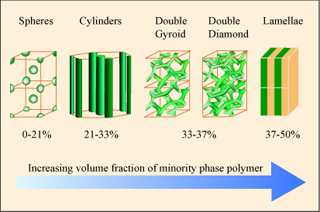
Composite material is a material made from two or more constituent materials with significantly different physical or chemical properties that, when combined, produce a material with characteristics different from the individual components Polymer composites are high-performance composites, framed using 3Dfabric reinforcement and shape memory polymer resin as the matrix. In consideration of shape memory polymer resin used as the matrix, these composites gain the potential to be easily engineered into variety of configurations when they are heated above their activation temperatures and will exhibit high strength and stiffness at lower temperatures. They can also be reheated and reshaped again without losing their properties. Polymer technology has an effective impact in developing advanced polymeric materials which are useful in day to day life. Composite material, the wonder materials are becoming an essential part of today’s materials due to the advantages such as low weight, corrosion resistance, high fatigue strength, and faster assembly. They are broadly used as materials in making aircraft structures, electronic packaging to biomedical equipment, and space vehicle to home building.
·Novel polymer composites
·Fly ash-based polymer matrix composites
·Conjugated polymers
·Conducting and shape memory polymers
·Natural and synthetic polymers
Polymer Physics
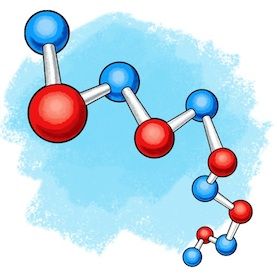
Polymer physics is the branch of physics which deals with polymers, their fluctuations, mechanical properties, polymer structures and also with the kinetics. Polymer physics encloses the physical properties, structure and dynamics of polymers (both synthetic and naturally occurring) in various forms including semi-crystalline solids, glasses, elastomers, gels, melts, and solutions. Basic phenomena are of interest in accordance with the applications of polymers in technologies, such as optoelectronics, photovoltaic, coatings, composites, medicine, food and pharmacy and tissue engineering.
·Ion-containing polymers
·Polymer Sensors
·Polymer blends/alloys
·Polymeric Light-emitting Diodes
·Electro active polymers
·Dielectric, optoelectrical and ferroelectric polymers
·Thermoplastic polymers
·Polymer colloids and gels
·Emulsion Polymers
·Polymeric Materials for Photonics
Role of Polymers in Biology and Biological systems
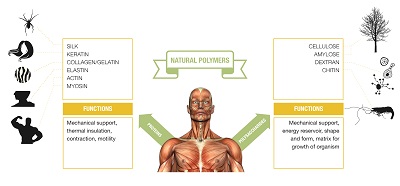
Biological macromolecules which are necessary for life include carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids, and proteins. These are the important cellular components and perform a wide array of functions necessary for the survival and growth of living organisms. These play a critical role in cell structure and function. Most biological macromolecules are polymers, which are any molecules constructed by linking together many smaller molecules, called monomers. Typically, all the monomers in a polymer tend to be the same, or at least very similar to each other, linked over and over again to build up the larger macromolecule. These simple monomers can be linked in many different combinations to produce complex biological polymers. The roles of macromolecules in living systems as information storage systems (as DNA) and in biochemical synthesis have been much studied and are relatively well understood and the roles of polymers in biological lubrication and its relation both to diseases such as osteoarthritis and to remedies such as tissue engineering. Protein polymers are available in large quantities in biology, and a huge variety of distinct filaments can be found and Protein mis-folding can be a route to pathological polymerization in diseases from Alzheimer’s to Parkinson’s. Synthetic polymers without difficulty can be formed from peptides and these are being studied for many causes, from forming new biomaterials to drug delivery/imaging. The demand for bio-based polymers is assumed to surge during the estimated period of 2015-2019 owing to the favorable regulatory outlook. The global biomarkers market is expected to reach US $45.55 Billion by 2020 from $24.10 Billion in 2015, at a CAGR of 13.58% through 2015 and 2020.
·Bio composites
·Bio elastomers
·Polymers in biotechnology
·Polymers for biosensors
·Polymers in crop plantation, protection and preservation
·Bioplastics & Biopolymers
·Bio-resorbable polymers
·Seed coating materials
Applications of Polymers
Polymers are a highly diverse class of materials which are available in all fields of engineering from avionics through biomedical applications, drug delivery system, bio-sensor devices, tissue engineering, cosmetics etc. and the improvement and usage of these depends on polymer applications and data obtained through rigorous testing. The applications of polymeric materials and their composites are still increasing rapidly due to their below average cost and ease of manufacture. This in turn fuels further development in research. Better understanding of the materials properties in diverse environments and temperature ranges is central to sourcing the correct polymer materials to suit the application.
·Biopolymers in molecular recognition
·Controlled drug release
·Polymers in bulletproof vests and fire-resistant jackets
·Food Packaging and processing Industry
·Organic polymer flocculants in water purification
·Polyolefins for health care industry
·Liquid polymer for car cleaning
·In aircraft, aerospace, and sports equipment
·Printed circuit board substrates
·Polymers in holography
·Printing plastics
Advanced Polymer Structures

Polymer science has always been research strength from thermoplastics to copolymers, thermosets to interpenetrating polymer networks, specialty polymers to composites and Nano composites. Through the period of three decades highly developed or complex polymer composites have come into existence as an attractive construction material for new structures and the strengthening/rehabilitation of currently existing buildings and bridges. The techniques related with the technology, analysis and design of polymer composites in construction are continually being researched and the advancement made with this exciting material will go on at an ever-rising rate to receive the demands of the construction industry. This advanced polymer finds applications not only in construction industry but also plays a major role in health, medicine and in biotechnology. In terms of revenue, the global advanced polymer structures market was valued at US$ 7.47 in 2013 and is expected to reach US$ 12.12 by 2020, expanding at a CAGR of 7.2% from 2014 to 2020.
·Polymer-metal hybrids
·Cyclic olefin copolymer structures
·Modelling/simulation of polymers
·Advanced polymer Synthesis and characterization methods
·Advanced elastomeric materials
·Smart & sustainable polymers
Polymers in wastes and their Environmental Impact

The traditional polymer materials are available today, especially the plastics, which is the result for decades of evolution. Their production is extremely efficient in terms of utilization of raw materials and energy, as well as of waste release. These products show an excellent property like impermeability to water and microorganisms, high mechanical strength, low density especially for transporting goods, and it is low-cost due to manufacturing scale and process optimization. However, some of their most useful features, the chemical, physical and biological inertness, and durability resulted in their accumulation in the environment if not recycled. Unfortunately, the accumulation of plastics, along with other materials, is becoming a serious problem for all countries in the world. These materials occupy significant volume in landfills and dumps today. Recently, the presences of huge amounts of plastic waste items are dumped into the oceans has been observed, considerable part of them coming from the streets, going through the drains with the rain, and then going into the rivers and lakes, and then to the oceans. These materials are harmful for living organism and it can affect the ecosystem too. So, these wastes should be recycled or managed under proper method. As a result, there is a very strong and irreversible movement, in all countries of the world, to use materials that do not harm the planet, that is, low environmental impact materials.
·Waste Items
·Classified Waste Materials
·Waste Management
·Recovery and Recycling of Organic Wastes
Market Analysis
Polymer Congress 2018 is the platform to gain or share the knowledge in the new technological developments in the field of Polymer Science and Technology. This conference brings together professors, researchers, scientists, students in all the areas of Polymer Science and provides an international forum for the spreading of approved research. We are honored to invite you all to attend and register for the “4th International Conference on Polymer Science &Technology (Polymer Congress 2018)” which is scheduled for June 4-5, 2018 at London, UK.
The organizing committee is gearing up for an exciting and informative conference program this year also which includes plenary lectures, symposia, workshops on a variety of topics, poster presentations and various programs for participants from all over the world. We invite you to join us at the Polymer Science Congress 2018, where you will be sure to have a meaningful experience with scholars from around the world. All members of the Polymer Congress organizing committee look forward to meeting you in London, UK.
Polymers plays a vital role in our lives because of its uniqueness in properties and extended application in industries, packaging, sports, medicine, perfumes and preservatives, plastics, fuels, toys etc. Polymer chemistry or macromolecular chemistry is concerned with the chemical synthesis and chemical properties of polymers. Polymer chemistry is a multidisciplinary science that deals with the chemical synthesis and chemical properties of polymers which were considered as macromolecules. Plastics are also used in the manufacture of Prosthetic devices and surgical equipment. Furthermore, polymer Science is quite a broad field and has expanded to include overlapping with Nanotechnology and materials science.
For more details please visit: http://polymerscience.euroscicon.com/
Major Polymer Science Associations around the Globe:
- American Chemical Society (Division of Polymer Chemistry)
- American Physical Society Division of Polymer Physics (APS DPOLY)
- Telford Polymer Association
- Polymer Coatings and Surfacing Institute
- Federation of Societies for Coatings Technology
- National Paint & Coatings Association
- Polymer Division of the Royal Australian Chemical Institute (RACI Polymer Division)
- The Polymer Society, UK
- American Plastics Council
- Association of Plastics Manufacturers in Europe
- European Committee of Machinery Manufacturers for the Plastics and Rubber Industries
- European Council for Plasticisers & Intermediates
- Indian Rubber Manufacturers Research Association
- Institute of Materials, Minerals and Mining
- Malaysian Plastics Manufacturers Association
- Performance Textiles Association
- The Polymer Society of Korea
- Polymer Machinery Manufacturers & Distributors Association (UK)
- Plastindustrieforbundet (Norway)
- Society of Plastics Engineers (USA)
- Society of the Plastics Industry (USA)
- European Polymer Dispersion and Latex Association
- British Plastics Federation
- Danish Chemical Society
- International Association of Nanotechnology
- Royal Society of Chemistry
- Society of Chemical Industry
- International Cast Polymer Alliance
- Polish Chemical Society
- Swedish Chemical Society
- Norwegian Chemical Society
- Faraday Society
- Royal Netherlands Chemical Society
- Hungarian Chemical Society
- Italian Chemical Society
- Association of Greek Chemists
- European Council for Plasticizers and Intermediates
- American Coatings Association
- Belgian Polymer Group (BPG)
- Brazilian Polymer Association
- The society for Polymer Science, India
- The society for Polymer Science, Japan
- Polymer Machinery Manufacturers and Distributors Association, UK
- European Polymer Federation
Target Audience
- Eminent Scientists of Polymer Science & Engineering
- Polymer Professors
- Research fellows
- Students
- Directors of Polymer companies
- Chemical Engineers
- Polymer Associations
- Nanotechnologists
- Materials Scientists
Top universities in London
- Imperial University
- University of London
- University of Westminster
- London South Bank University
- Middlesex University
- Central Saint Martins
- Brunel University London
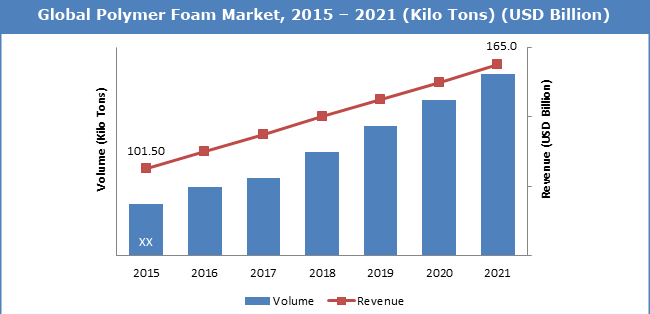
Glance at Market of Polymer Science
The plastics industry shapes the world we live in today whether it is industrial, technological or commodities used on a regular basis. A recent research has been carried out which covered a wide spectrum of plastics including materials, additives, processes, applications, and inter materials. Polymers, resins, coatings, films and composites are major areas of the plastics market covered. Quality market analysis, forecasts and trends determined from key market drivers help shape the future of the plastics industry. In-depth company profiles and patent analysis will help understand the emerging technologies and applications by key market players and stakeholders.
The global reinforced plastic composite market will grow from 14.8 billion pounds to about 17.6 billion pounds by 2020, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 3.5% for the period of 2015-2020.The global market for cast polymers reached 209.7 million square meters in 2014.This market will grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 9.5% to reach 361.5 million square meters in 2020 from 229.2 million square meters in 2015 for the period 2015-2020. Global consumption of fluoropolymers amounted to 702.7 million lbs. in 2014 and is projected to total 740.4 million lbs. in 2015. The market is expected to grow during the period 2015 to 2020 at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.5% to reach 969.1 million lbs. in 2020.The U.S. medical plastics market totaled nearly 4.4 billion pounds in 2014. This market should reach nearly 4.6 billion pounds in 2015 and 5.8 billion pounds by 2020 increasing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.8% between 2015 and 2020.The global market for glass fiber reinforced plastics will grow from $31.4 billion in 2014 to nearly $44.4 billion by 2019 at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.1% between 2014 and 2019.The overall U.S. market for polymeric flexible hose and tubing materials was over 1.0 billion pounds in 2015 and should reach 1.1 billion pounds in 2020 at a five-year compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 2.4%.The global market for thermoformed plastics reached nearly 8.0 billion pounds in 2015. The market is expected to reach 10.2 billion pounds by 2021 from nearly 8.3 billion pounds in 2016, increasing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.3% from 2016 to 2021.The global market for plastics additives was valued at $48.2 billion in 2015. This market is estimated to grow from nearly $50.6 billion in 2016 to $64.6 billion by 2021 with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.0 % for the period of 2016-2021.The U.S market for polymeric foam was nearly 7.9 billion pounds in 2014. This market is predicted to reach nearly 8.1 billion pounds in 2015 and nearly 9.3 billion pounds in 2020, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 2.8%. The global engineering resin and polymer alloy/blend market reached 24.1 billion pounds in 2014. The market is projected to increase to over 25.2 billion pounds by 2015 and nearly 31.4 billion pounds in 2020, with a compound annual growth rate of 4.5%.
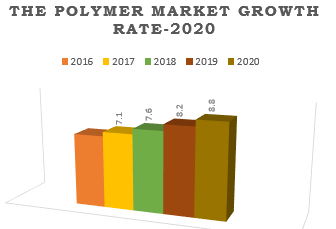
Estimated Global Polymer Market Growth Rate by 2020:
The Global High-Performance Polymers Market is poised to grow at a CAGR of around 6.5% in the next 5 years to reach approximately $8.8 billion by 2020. he studies focuses on market trends, leading players, supply chain trends, technological innovations, key developments, and future strategies. The report provides comprehensive market analysis across four major geographies such as North America, Europe, Asia Pacific and Other parts of the world
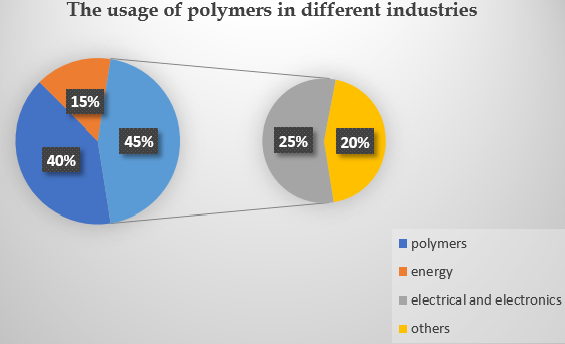
Polymers occupy a prominent role in this modern living. From the tooth brush, lunchboxes, toys, pens etc. to a lot of products are being used everyday life. It is absolutely Wondering, when we understand the polymers and its utmost functionalities. From the daily utilities to the most advanced areas of research, polymer is a fundamental component. Man synthesized artificial polymer mimicking the natural polymers, which is a group of molecules combined. The polymers have a great future ahead because of its increased demand and usage. Researches are being carried out to use polymers more effectively now days. In the field of biology and pharma, more artificial organs of humans are being produced to help the humanity. The polymers will also combine with Nano science, to occupy less mass. The Aerospace also use significant quantity of modern polymers for the construction of the spaceship, and machinery items.
Learn More
Leibniz Institute of Polymer Research Dresden| Postnova Analytics GmbH |Addlink software cientifico | CK Polymers| Advanced Technologies Center ATC | Magpie Polymers| Living Cell Technologies | Micro-Bio-Polymer Company | Evolve Polymers Limited | Meric Ltd|Quick step Technologies | VSPC co.LTD | Warsash scientific | AQUANOVA AG | Gyros| Membracon Process Separations|EPC Engineering Consulting GmbH |VIP Polymers Ltd | nDure Technologies | Ingenia Polymers Corp. |Quick step Technologies | Gioco Solutions Sr l CETCO Energy Services | Dr. Jens Naehring| POLYMERS & COLORS S.A. | NOXON AB |HETA Verfahrenstechnik GmbH|Polymer Characterization, S.A |Aquamarijn micro filtration | Triple Benefit |Fuglesangs AS | Ceramic Polymer GmbH| CCM | Recycling Technology Ltd |ASM International | Aquafide Engineering Limited | General Polymeren Recycling Albania |Finex Oy | Mert Döküm|Avantium | Delmic | Universal HDD| SABIC | European Plastics Recyclers|DSM somos | Buss-SMS-Canzler GmbH|HQ graphene| Aquafil Spa | MEA Water Management GmbH | IME Technologies | JUTA a.s. |KRIYA Materials| Holstcentre| Terratech Inc| Industrial Rubber Limited | Hobas Pipe USA |CPS Instruments |Euroscicon| SchuF Fetterolf |Photonic Cleaning Technologies, LLC |Micronitechnologies|2DTECH|3M ESPE | AHS | agar scientific | SUMI Recycling |Applied graphene materials | Euroscicon| Aquila instruments | Solvay S.A.|Chained Labs| BBI solutions | Bucchi S.r.l. | Bio Polymer consulting | Digisens 3D Tomography Software Solutions | Perstorp | Applied Felts Inc.| Stamixco AG| Cambridge Display Technology| Carbolite gero | Renishaw apply innovation | Dolomite| Ellit Scientific solution science for research and industry | Elementsix | HEG Engineering GmbH| C L Rye Trading Ltd. | Edinburgh Instruments | Durham| Magneto optics Ltd |Antaria Limited | Hutchinson Worldwide |Eurochem specialist chemicals | Biolin Scientific | Fischer Instrumentation | Ad-particles | CilaZ | Avanzare | Izasa scientific | Gemini Israel Ventures | Nadetech Innovations| Graphene Tech | Auto Car Brands | ABC-Miljø|Leblog auto | WTS Global | BR Automation | AGM Automation System Inc | AGI Automation Components | Aveni| Kobus | CS Instruments | Cordouan Technologies | Malvern Instruments Ltd|Huntsman Advanced Materials | Biokowski psb Industries | Fluigent Smart Microfludics | Digital Surf Birds Contract Services| Silvaco | Schambeck SFD GmbH| Ceramisphere Ltd|Marion Technologies | LIST Technology AG | General Industries | ABCR supplies Lmtd | AIXTRON | Buhler | Bayer|Crop Science AG| Bio Gate | BIONI | BYK Additives&Instruments |Coral Products| Bayer Crop Science AG| Bartels | BASF | Cadfem|Bayer | Umicore S.A. |Umicore Recycling Solutions |Centech | B-Team Corrosion Protection|DYESOL | Zeiss| Quadrant EPP UK Ltd| Advanced Magnetic Technologies & Consulting Group | Concern Polymer industry | Interface Ltd | NT-MDT | Russian Corporation of Polymer technology | A.P.E. Research |Peroxy Chem| LyondellBasell | Directa Plus | Linari Biomedical | MBN | Mindseeds Laboratories | Organic Spintronics | Plasma Diagnostics and Technologies | SCRIBA | Dimple-t Bulk Solids Cooler | Inan Plastics Makinalari San| Silicon Biosystems | First Water Limited| Xenia Materials | Collaborative Centre for Applied | Dinworks OY|PLIN | Deerac Fluidics | Polymer Diamond Products | Sireg Geotech S.r.l | Particular Sciences | Beaulieu Technical Textiles |Proviron| Sampas | KPlus| Kunststoftechniek | ACO Group| ABB Groups | Trelleborg Forsheda Pipe Seals| Smithers Rapra| Buhler Group | Novo Polymers NV | Kiss Soft | Greater Zuricharea | NBM | Optical Additives | PSI | Solectron | Agfa | CMI Group | Waters Smart Innovations | Tec Concept | Silex micro Systems | PFSW | BASF| Ekotakas| UAB| Trendelkamp Technologie GmbH | ECO Engineering Ukraine LLC |Euroscicon Conferences
Angstrom Engineering | Braskem |Dow Chemical| A&A coatings | Sinopec | Praxair| 30 SK Innovation| LG Chem| ACS Materials | SABIC| Innovative Bioceremix,Inc | Arkema| ADA technologies | Asahi Kasei| Mosaic| Ade 10 Angstroms| Lanxess | Huntsman Corp.| Advanced Diamond Solutions | Indorama| AEB| Sasol| Advanced Energy| ExxonMobil| Borealis| Advance TEC | ADVANO | Advenira solutions | Siam Cement| DIC |Eastman Chemical |Air Liquide |Aegis Technologies | LyondellBasell Industries| Hanwha Chemical|Formosa Plastics |3D systems | DSM |PTT Global Chemical |Euroscicon| American Dye Source, Inc.| Bayer| Tosoh| Syngenta| DuPont| ClemexTechnologies Inc | AkzoNobel| Shin-Etsu Chemical| Air Products & Chemicals| Cytodiagnostics Inc.| Reliance Industries|Evonik Industries| BP|Euroscicon| Solvay |Mitsui Chemicals|D-Wave Systems | Delong America group Inc| Electronics.ca Publications | Shell| Ineos| Epoc Blood Analyst System | Johnson Matthey| Lotto Chemical | Klean Carbon | MCH soloutions | MFS | Ecolab Technologies Ltd | IMEMS | 4WAVE | Sumitomo Chemical| Linde| Toray Industries| Advance Reproductions | Advanced optical technologies| Indigo Instruments| Applied Polymer tools Inc. | A Beam Technologies|Mitsubishi Chemical| Yara| PPG Industries| Chevron Phillips Chemical |Euroscicon Conferences
Polymer Companies in Asia and Middle East:
Amphenol | Helios Applied Systems | Itochu Systech | Abacusnext Curtiss-Wright | Proactive Investors Alpha Casting | NOF CORPORATION | CNC Machining | Molecular Rubber| Design | Interaction Point | Knights Security | United Plastic |Polymer Industries Ltd| Innovation Kaust | Shida Rubber | Digit Link | Tiny Machining | Precision Type | Bugatti| Aixam | PACIFIC COAST | FM Global | ISAT | Polymer Infrastructure | Comtech Advanced | Incubation Alliance | Image Sourcing ATIP|HSRE Work | ICAM | Egypt Polymer center | Digital Guadian | Proteck Coating |Euroscicon| Huper optic| ATKINS Group | Polymer materials technology| Polymer Center | V-kool | Polymer yo | |Curiox Accelerating life Sciences |Fuji Xerox | Marubeni | Society of Petroleum Engineers | Alienvault | Showa Denko | Taisei Kogyo | Micron | SBEC | BMVIT | AIT | Polymer Enterprise | SSV | KSU | Green Prophet | F- Carbon | Lake Central | Gobiz Korea | Quantum| MR Sourcing | Polymer Technology | Polymer Solutions| Euroscicon Conferences
Postdoctoral Researcher in Polymer Chemistry and Materials Group | Senior Researcher Optical | Team Leader jobs Physical Design|Design Automation and Mask Data Preparation | Program Manager jobs | R&D Engineer Career Wet etch/clean |Process Integration Engineer FEOL | Postdoc Project leader| Process Engineer Device Fabrication Career | Polymer science postdoctoral positions Career |Senior Scientist - Dynamic Materials Response career| Polymer science postdoctoral positions Jobs | Control of the Polymer mechanics of Viral and Bacterial Infections jobs | Assembly Technician Jobs|Postdoc Jobs in Silicon micro- and Polymer fabrication for catalyst studies |PhD position in the Polymer Chemistry Group Jobs |MEMS Operations Director Jobs |Euroscicon| Director of Polymer technology Jobs Core Facility |Manager, Microelectronics Fabrication Laboratory Jobs | Physical Scientist – Polymer technology Career |Lecturer career in Experimental Condensed Matter Physics |Computational Chemist Career| Image Sensor Measurement Set-up Development Engineer jobs |Senior Process Integration Engineer Wafer Fabrication Jobs |Production Technician Career | Team Leader Jobs Imager Design|Senior Process Engineer CMP and Plating|Postdoc on Quantum Computing |Postdoctoral Researcher Jobs on Mixed Signal Circuit Design f
Others

What is a polymer?
A polymer (Greek poly-, "many" + -mer, "parts") is a large molecule, or macromolecule, composed of many repeated subunits. Because of their broad range of properties, both synthetic and natural polymers play essential and ubiquitous roles in everyday life.Polymers range from familiar synthetic plastics such as polystyrene to natural biopolymers such as DNA and proteins that are fundamental to biological structure and function. Polymers, both natural and synthetic, are created via polymerization of many small molecules, known as monomers. Their consequently large molecular mass relative to small molecule compounds produces unique physical properties, including toughness, viscoelasticity, and a tendency to form glasses and semicrystalline structures rather than crystals.
The term "polymer" derives from the ancient Greek word πολÏς (polus, meaning "many, much") and μÎρος (meros, meaning "parts"), and refers to a molecule whose structure is composed of multiple repeating units, from which originates a characteristic of high relative molecular mass and attendant properties. The units composing polymers derive, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass. The term was coined in 1833 by Jöns Jacob Berzelius, though with a definition distinct from the modern IUPAC definition. The modern concept of polymers as covalently bonded macromolecular structures was proposed in 1920 by Hermann Staudinger, who spent the next decade finding experimental evidence for this hypothesis.
Polymers are studied in the fields of biophysics and macromolecular science, and polymer science (which includes polymer chemistry and polymer physics). Historically, products arising from the linkage of repeating units by covalent chemical bonds have been the primary focus of polymer science; emerging important areas of the science now focus on non-covalent links. Polyisoprene of latex rubber is an example of a natural/biological polymer, and the polystyrene of styrofoam is an example of a synthetic polymer. In biological contexts, essentially all biological macromolecules—i.e., proteins (polyamides), nucleic acids (polynucleotides), and polysaccharides—are purely polymeric, or are composed in large part of polymeric components—e.g., isoprenylated/lipid-modified glycoproteins, where small lipidic molecules and oligosaccharide modifications occur on the polyamide backbone of the protein.
( Ref: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Polymer)
How are Polymers made?
Synthetic polymers are produced by chemical reactions, termed "polymerizations." Polymerizations occur in varied forms--far too many to examine here--but such reactions consist of the repetitive chemical bonding of individual molecules, or monomers. Assorted combinations of heat, pressure and catalysis alter the chemical bonds that hold monomers together, causing them to bond with one another. Most often, they do so in a linear fashion, creating chains of monomers called polymers.Some polymerizations join entire monomers together, whereas others join only portions of monomers and create "leftover" materials, or by-products. Co-polymers can be formed using two or more different monomers. And two or more polymers can be combined to produce an alloy, or blend, that displays characteristics of each component.
For an example, let's consider the common plastic polyethylene, which is found in such items as grocery bags, toys and bottles. The monomer ethylene is composed of two carbon atoms, each bonded to two hydrogen atoms and sharing a double bond with one another. Polyethylene consists of a chain of single-bonded carbon atoms, each still carrying its two hydrogen atoms.
LINEAR POLYETHYLENE
One way to produce polyethylene is called "free radical polymerization." As in other polymerizations, the process has three stages, known as initiation, propagation and termination. To begin, we need to add a catalyst to our supply of ethylene. A common catalyst is benzoyl peroxide, which when heated has the habit of splitting into two fragments, each with one unpaired electron, or free radical. These fragments are known as initiator fragments.
The unpaired electron naturally seeks another and finds a convenient target in the double bond between the carbon atoms in the ethylene molecule. Taking an electron from the carbon bond, the initiator fragment bonds itself to one of the monomer's carbon atoms.
The radical is now happy, but this initiating reaction creates another free radical associated with the ethylene molecule's other carbon atom. The new radical also seeks a partner. And so ethylene monomers begin attaching themselves in a chain, creating new radicals each time and lengthening the chain. This stage is called propagation.Growing chains may also attach themselves to one another. Most commonly, chains join end to end, but sometimes they join end to backbone, making branched polyethylene molecules.
Eventually, free radical polymerization stops due to what are called termination reactions. For example, instead of stealing an electron from double-bonded carbons or a nearby propagating chain, the carbon atom with the free radical sometimes steals an entire hydrogen atom from another chain end. The polymer end--robbed of its hydrogen--easily forms a double bond with its adjacent carbon atom, and polymerization stops.
Because every part of the ethylene monomer is included in the finished polymer, the free radical polymerization of polyethylene is referred to as an addition polymerization; the ethylene molecules are simply added together. Polymerizations that use only portions of a monomer, however, are known as condensation polymerizations. The monomers that condense with each other must contain at least two reactive groups in order to form a chain. Condensation reactions result in "condensed" polymers that have less total mass than the monomers used to create them and the by-products, or "condensates," combined.
For example, poly(ethyleneterepthalate), a polyester known as PET that is commonly found in soda bottles, forms from a reaction of two monomers: ethylene glycol and terephthoyl chloride. At the reaction's end, an atom of hydrogen and an atom of chlorine are left out of each PET molecular junction, resulting in a by-product of hydrogen chloride (HCl) gas.
(Ref: https://www.scientificamerican.com/article/how-are-polymers-made/)








































